All of the following are true of ribosomes except they are found only in eukaryotic cells sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
Ribosomes, the protein synthesis machinery of the cell, are fascinating organelles with a complex structure and a crucial role in cellular function. This article delves into the intricacies of ribosomes, exploring their composition, location, function, regulation, and clinical significance, providing a comprehensive overview of these essential cellular components.
Ribosomes are composed of two subunits, a large subunit and a small subunit, each of which is composed of a combination of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. The rRNA molecules provide the structural framework of the ribosome, while the proteins are responsible for its catalytic activity.
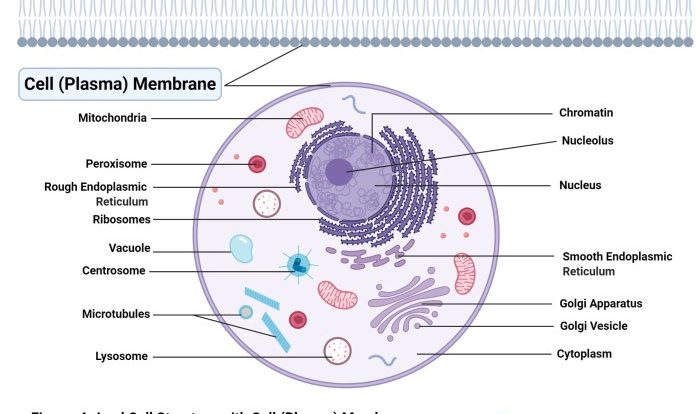
Ribosomes are located in both the cytoplasm and the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) of eukaryotic cells, and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells.
Structural Components and Composition

Ribosomes are complex molecular machines composed of both ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. rRNA constitutes the majority of the ribosome’s mass, while proteins provide structural support and facilitate interactions with other cellular components. The ribosome consists of two subunits, a large subunit and a small subunit, which assemble to form a functional ribosome.
Ribosomal RNA
rRNA is a type of non-coding RNA that plays a crucial role in ribosome structure and function. It provides a scaffold for the assembly of ribosomal proteins and facilitates the formation of the ribosome’s catalytic center. rRNA also interacts with mRNA and tRNA during the process of protein synthesis.
Ribosomal Proteins
Ribosomal proteins are essential for the structural integrity and function of ribosomes. They bind to rRNA and help stabilize the ribosome’s structure. Additionally, ribosomal proteins interact with other cellular components, such as translation factors and elongation factors, to facilitate the process of protein synthesis.
Structure of the Ribosome, All of the following are true of ribosomes except
The ribosome has a complex and highly organized structure. The large subunit contains three tRNA binding sites: the A site, the P site, and the E site. The small subunit contains the mRNA binding site and the decoding center, where the ribosome reads the genetic code in mRNA.
Question Bank: All Of The Following Are True Of Ribosomes Except
What are ribosomes?
Ribosomes are cellular organelles responsible for protein synthesis.
Where are ribosomes located?
Ribosomes are located in both the cytoplasm and the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) of eukaryotic cells, and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells.
What is the function of ribosomes?
Ribosomes are responsible for translating genetic information into proteins.