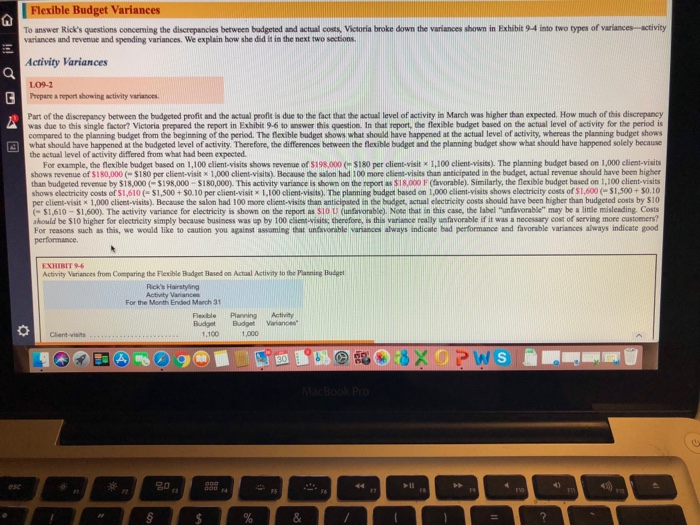
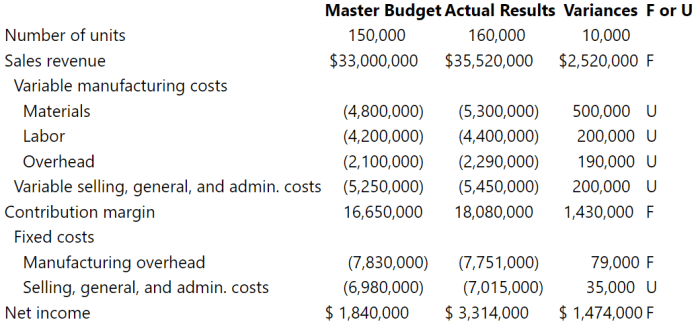Unfavorable activity variances may not indicate bad performance because they fail to account for external factors, temporary setbacks, and the broader context of strategic objectives, market conditions, and resource constraints. It is essential to consider multiple performance metrics and non-financial indicators to accurately assess overall effectiveness.
Activity variances, while useful for identifying deviations from planned activity levels, should not be the sole determinant of performance evaluation. Other factors, such as strategic objectives, market conditions, and resource constraints, must also be considered to provide a more comprehensive assessment.
Activity Variances: Definition and Causes: Unfavorable Activity Variances May Not Indicate Bad Performance Because
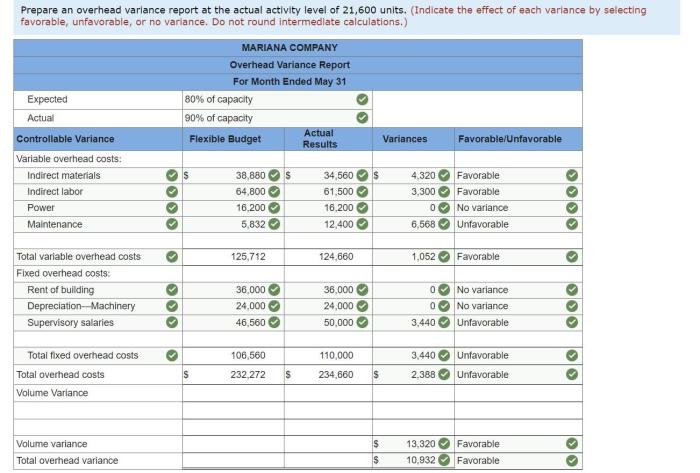
Activity variances are performance metrics that measure the difference between actual and budgeted levels of activity. They can be used to assess the efficiency and effectiveness of operations. Unfavorable activity variances indicate that actual activity levels were lower than budgeted, which can be a sign of operational inefficiencies or other issues.
Various factors can contribute to unfavorable activity variances, including:
- Changes in customer demand
- Inefficient production processes
- Poor planning and scheduling
- Employee absenteeism
- Equipment breakdowns
Performance Assessment Beyond Variances
While activity variances can provide valuable insights into operational performance, it is important to avoid relying solely on these metrics for performance evaluation. Other factors, such as strategic objectives, market conditions, and resource constraints, should also be considered.
For example, a company may experience an unfavorable activity variance due to a decline in customer demand. However, this variance may not necessarily indicate poor performance if the company has successfully adapted to the changing market conditions and maintained profitability.
Unfavorable Variances in Context
There are situations where unfavorable activity variances may not indicate poor performance. For instance:
- External factors:Unforeseen events, such as natural disasters or economic downturns, can significantly impact activity levels.
- Temporary setbacks:Temporary disruptions, such as equipment breakdowns or employee training, can lead to short-term unfavorable variances.
- Strategic decisions:Companies may intentionally reduce activity levels to focus on long-term goals, such as product development or market expansion.
Measuring True Performance, Unfavorable activity variances may not indicate bad performance because
To assess overall effectiveness, it is crucial to use multiple performance metrics. Non-financial indicators, such as customer satisfaction, employee engagement, and innovation, can provide a more comprehensive view of performance.
By considering a range of metrics, managers can gain a deeper understanding of the factors that are driving performance and make more informed decisions.
Implications for Management
Managers should interpret unfavorable activity variances with caution and analyze the underlying causes. Appropriate actions should be taken to improve performance, such as:
- Identifying and addressing inefficiencies
- Improving planning and scheduling
- Investing in employee training and development
- Monitoring market conditions and adapting accordingly
Common Queries
What are activity variances?
Activity variances measure the difference between actual activity levels and planned activity levels.
What are the limitations of using activity variances for performance evaluation?
Activity variances do not account for external factors, temporary setbacks, or the broader context of strategic objectives, market conditions, and resource constraints.
What are some examples of situations where unfavorable activity variances may not indicate poor performance?
Unfavorable activity variances may not indicate poor performance if they are due to external factors, such as a recession, or temporary setbacks, such as a production delay.
What are some other factors that should be considered when evaluating performance?
Other factors that should be considered when evaluating performance include strategic objectives, market conditions, resource constraints, non-financial indicators, such as customer satisfaction and employee engagement.